Packages’ installation in R
R packages are collections of functions and dataset developed by their authors.
What are repositories?
A repository is a plcae where packages are located so you can install them from it. Although you might have a local repository, typically R packages are located at remote servers and you can install them online. There are three most popular repositories for R as following:
- CRAN: the official repository, it is a network of ftp and web servers maintained by the R community around the world. The R foundation coordinates it, and for a package to be published here, it needs to pass several tests that ensure the package is following CRAN policies. You can find more details here.
- Bioconductor: this is a topic specific repository, intended for open source software for bioinformatics. As CRAN, it has its own submission and review processes, and its community is very active having several conferences and meetings per year.
- Github : although this is not R specific, Github is probably the most popular repository for open source projects. Its popularity comes from the unlimited space for open source, the integration with git, a version control software, and its ease to share and collaborate with others. But be aware that there is no review process associated with it.
How to install An R Package
Install an R package from CRAN
1
install.packages("vioplot")
Install it from a specific repository (CRAN mirrors). You can select your micro by using chooseCRANmirror()or just adding “repo”parameter after install.package
1
2
install.packages("vioplot", repo = "https://lib.ugent.be/CRAN/")
or change “repo” to Tsinghua’s mirror
1
install.packages("vioplot", repo = "https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/CRAN/")
Install R package from Bioconductor
1
BiocManager::install("DESeq2")
The first thing to do is checking what kind of proxy you’re using. I’m using V2ray now, so check it’s configure:
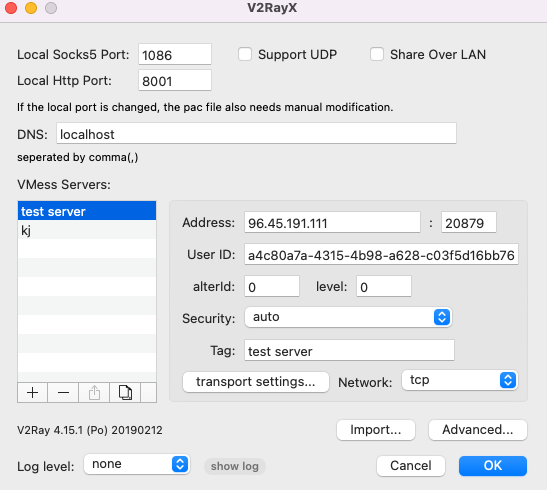
Open Terminal and code the following:
1
vim ~/.Renviron
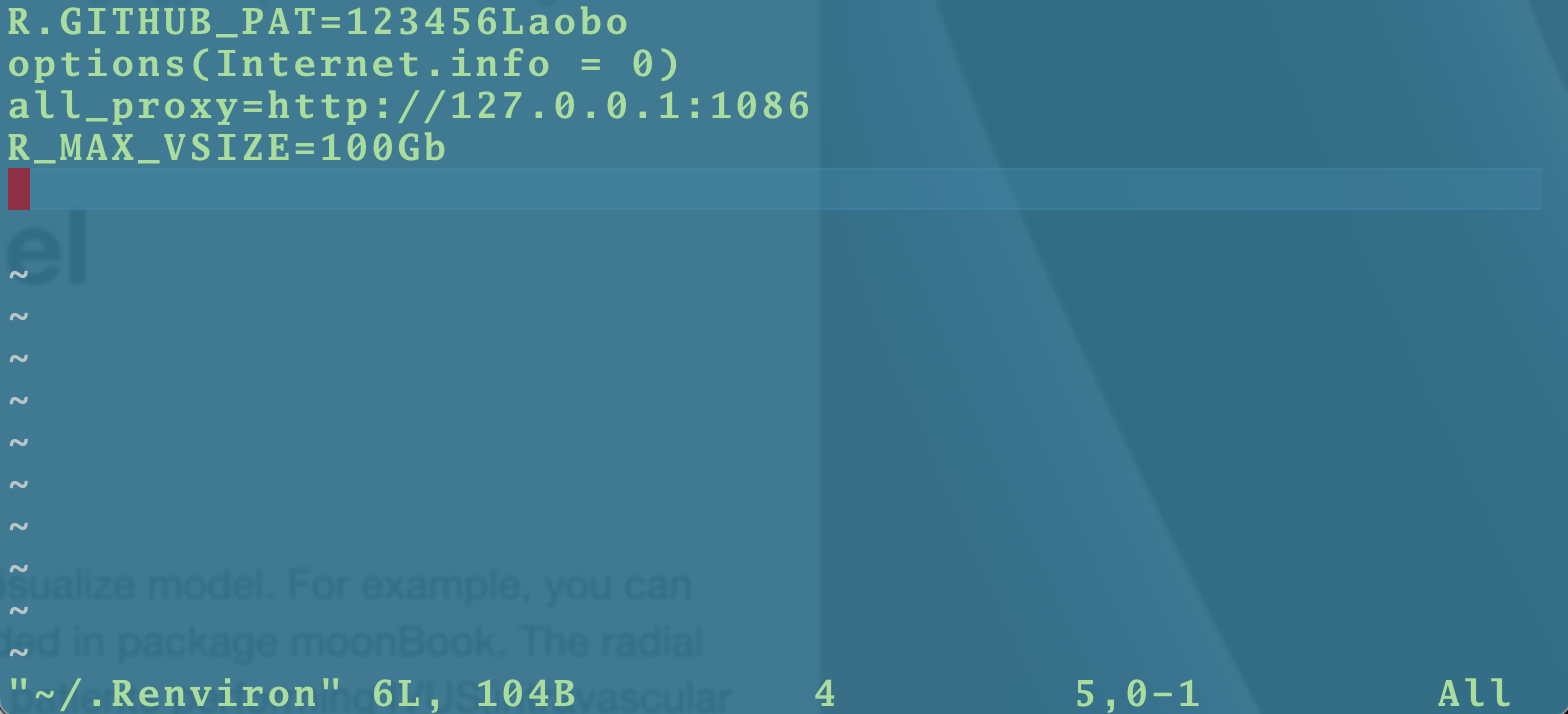
Save it . Done!
If the above resolution doesn’t work, try this at Rstudio: using http proxy
1
Sys.setenv(all_proxy="http://127.0.0.1:8001")
If you want to remove this variable:
1
Sys.unsetenv("all_proxy")
Can not install packages from GitHub using devtools::install_github()? Try the following codes:
1
2
3
options(download.file.method = "libcurl") # or you can change the "libcurl" to "wget", which just works for me
options(download.file.method = "wget")
Damn it
It’s often occurred that you can not install any packages using BiocManager:install when you’re setting proxy in R. What the hell it is going on here?
1
Sys.setenv(all_proxy="http://127.0.0.1:8001")
However, if you remove this setting, it will work normally!
1
Sys.unsetenv("all_proxy")
I may need to figure it out how proxy in R work.
Download a file from Internet
wget vs curl
curl is a command line tool and a library which can be used to receive and send data between a client and a server over the internet. curl supports a wide range of protocols such as HTTP/HTPPS, FTP, IMAP, LDAP, POP3, etc. Owing to its versatile traits, curl has been used in many applications and for many use cases. For examples, it can be used to download files, testing APIs and checking network problems.
Install curl in macOS:
1
brew install curl
For instance, the following command will receive the HTML page from baidu.com.
1
curl http://baidu.com > test.html
If without >test.html, curl receive the HTML page and directly print it to the screen of terminal. Alternatively, you can use the -0 option, like
1
curl -o test.html http://baidu.com
You can also try wget
1
wget http://baidu.com
By default, wget will download the HTML page into a file.
wget can not support socks